Introduction
Text formatting is a crucial skill for Linux users, whether you’re preparing documents for printing, organizing data, or creating readable output. This comprehensive guide will explore the essential Linux commands for formatting output, including nl, fold, fmt, pr, printf, and groff.
Understanding Basic Text Formatting Commands
The nl Command: Line Numbering Made Easy
The nl command is a powerful tool for adding line numbers to text files. Here’s how to use it effectively:
# Basic usage
nl filename.txt
# Number only non-blank lines (default)
nl -b t filename.txt
# Number all lines
nl -b a filename.txtKey Features:
- Supports logical page concepts (header, body, footer)
- Customizable number format and separator
- Flexible line selection for numbering
The fold Command: Managing Line Width
fold helps wrap text to specific line lengths, essential for formatting text for different display environments:
# Wrap lines to 80 characters
fold -w 80 filename.txt
# Wrap at spaces (avoid breaking words)
fold -s -w 80 filename.txtThe fmt Command: Smart Text Formatting
fmt is a versatile text formatter that handles paragraphs intelligently:
# Format text to 50 characters width
fmt -w 50 filename.txt
# Format while preserving indentation
fmt -c -w 50 filename.txtAdvanced Formatting Tools
The pr Command: Preparing Text for Printing
pr transforms text files for printing with features like:
- Page headers and footers
- Multi-column output
- Page numbering
- Margin control
Example usage:
# Create paginated output with headers
pr -h "My Document" -l 60 filename.txt
# Create multi-column output
pr -2 filename.txtThe printf Command: Precise Output Control
printf offers C-style formatting capabilities:
# Basic string formatting
printf "Name: %s\nAge: %d\n" "John" 25
# Number formatting
printf "%.2f\n" 3.14159Common format specifiers:
%s- Strings%d- Integers%f- Floating-point numbers%x- Hexadecimal
Document Formatting with groff
Introduction to groff
groff is a powerful document formatting system that can produce:
- Man pages
- PDF documents
- PostScript output
- ASCII text
Basic example:
# Create a simple formatted document
groff -man -T ascii document.1 > output.txtWorking with Tables in groff
Using the tbl preprocessor:
# Format tables in groff
tbl input.txt | groff -T asciiYour Turn!
Try this practical exercise:
Problem: Create a formatted table of system information using printf.
Click here for Solution!
Solution:
#!/bin/bash
printf "%-20s %-10s %-15s\n" "HOSTNAME" "MEMORY" "DISK USAGE" $(hostname) "$(free -h | awk '/^Mem:/ {print $2}')" "$(df -h / | awk 'NR==2 {print $5}')"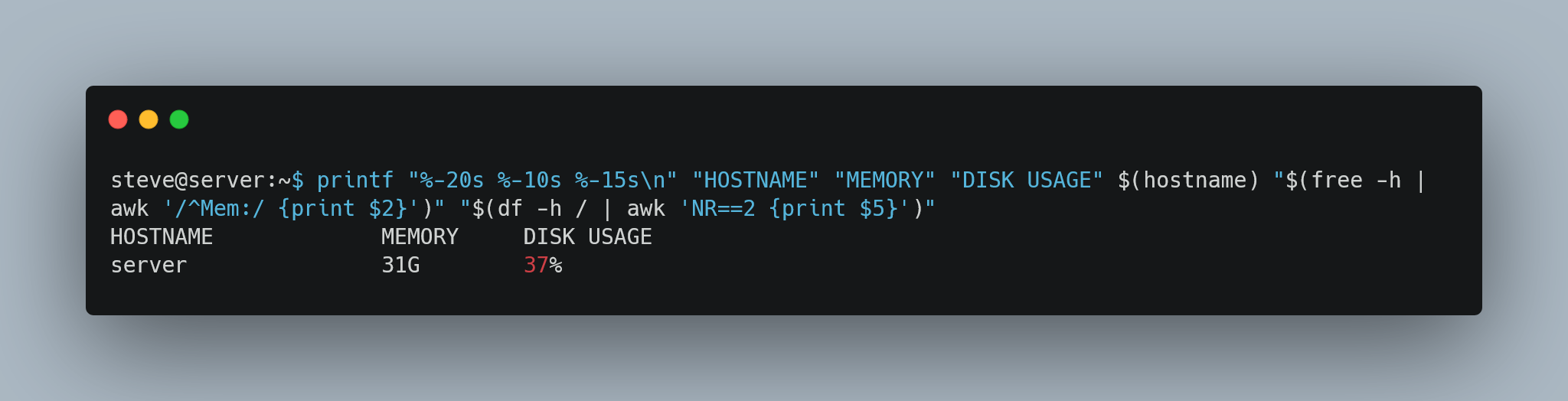
Quick Takeaways
- Use
nlfor line numbering foldfor controlling line widthfmtfor paragraph formattingprfor pagination and printing preparationprintffor precise output controlgrofffor professional document formatting
FAQs
Q: Which command should I use for simple text wrapping? A: Use
foldfor basic text wrapping, orfmtif you need more intelligent paragraph formatting.Q: How can I add line numbers to a file while excluding blank lines? A: Use
nl -b t filename.txtQ: Can I format tables without using groff? A: Yes, you can use
printforcolumnfor simple table formatting.Q: How do I create PDF output from formatted text? A: Use groff to create PostScript output, then convert it using ps2pdf.
Q: What’s the difference between fmt and fold? A:
fmtis paragraph-aware and preserves indentation, whilefoldsimply wraps text at specified widths.
References
- Linux Handbook - Understanding fold and fmt Commands
- GeeksforGeeks - fmt Command in Unix/Linux
- Opensource.com - fmt: The Trivial Text Formatter
We hope you found this guide helpful! Please share it if you found it useful, and leave a comment with any questions or suggestions.
Happy Coding! 🚀

You can connect with me at any one of the below:
Telegram Channel here: https://t.me/steveondata
LinkedIn Network here: https://www.linkedin.com/in/spsanderson/
Mastadon Social here: https://mstdn.social/@stevensanderson
RStats Network here: https://rstats.me/@spsanderson
GitHub Network here: https://github.com/spsanderson
Bluesky Network here: https://bsky.app/profile/spsanderson.com
My Book: Extending Excel with Python and R here: https://packt.link/oTyZJ